Quick actions
Stay organised
Bookmark tricky derivations, add doubts to your dashboard, and revisit them before tests.
Open dashboard →NCERT Solutions for class 10 Science Chapter 11:Human Eye and Colourful World
Review "Human Eye and Colourful" with concise NCERT answers and quick tips.
Exercise Question
Question 1
The human eye can focus objects at different distances by adjusting the focal length of the eye lens. This is due to(a) presbyopia
(b) accommodation
(c) near-sightedness
(d) far-sightedness
Answer
(b) accommodation
Question 2
The human eye forms an image of an object at its(a) cornea
(b) iris
(c) pupil
(d) retina
Answer –
(d) retina
Question 3
The least distance of distinct vision for a young adult with normal vision is about(a) 25 m
(b) 2.5 cm
(c) 25 cm
(d) 2.5 m
Answer –
(c) 25 cm
Question 4
The change in focal length of an eye lens is caused by the action of the(a) pupil
(b) retina
(c) ciliary muscles
(d) iris
Answer
(c) ciliary muscles
Question 5
A person needs a lens of power -5.5 dioptres for correcting his distant vision. For correcting his near vision he needs a lens of power +1.5 dioptre. What is the focal length of the lens required for correcting (i) distant vision, and (ii) near vision?Answer
We know Power of lens (P) =(i) Power of the lens for correcting distant vision = – 5.5 D
Sof =
ii)
The focal length is – 0.181 m.
(ii) Power of the lens for correcting near vision = +1.5 D
We know Power of lens (P) =The focal length is 0.667 m.
Question 6
The far point of a myopic person is 80 cm in front of the eye. What is the nature and power of the lens required to correct the problem?Answer
When the image is formed in front of the retina then person is suffered from myopia.So concave lens is used to correct this defect of eyes.
Let object distance is infinity
Image distance v = – 80 cm
Focal length = f
Using lens formula,
f =-80 m
We also know
p =
p
power of concave lens is – 1.25 D
Question 7
Make a diagram to show how hypermetropia is corrected. The near point of a hypermetropic eye is 1 m. What is the power of the lens required to correct this defect? Assume that the near point of the normal eye is 25 cm.Answer
When we see distinct objects clearly but difficulty to see nearby object due which image form beyond the retina of eyes then the person suffer from hypermetropia.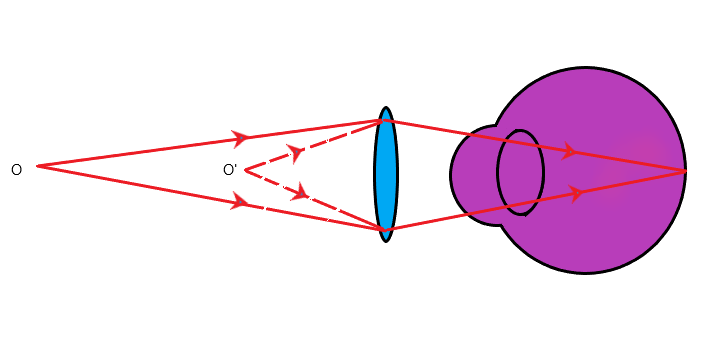
Given
Object distance, u = – 25 cm
Image distance, v = – 1 m = – 100 m
Focal length f
Using the lens formula,
f =
f =33.3cm = 0.33m We also know
p =
p
Power of convex lens +3.0 D.
Question 8
Why is a normal eye not able to see clearly the objects placed closer than 25 cm?Answer
This is due to ciliary muscles of the eyes are unable to contract beyond a certain limit.
Question 9
What happens to the image distance in the eye when we increase the distance of an object from the eye?Answer
Due to accommodation our eyes can increase or decrease the focal length so that the image is formed on the retina .So there is no effect on image even on increasing the distance of an object from the eye.
Question 10
Why do stars twinkle?Answer
The twinkling of a star is due to atmospheric refraction of starlight. The starlight, on entering the earth’s atmosphere, and reaching our eyes change continuously and stars appear to twinkle.
Question 11
Explain why the planets do not twinkle?Answer
The planets are much closer to the earth, and a collection of a large number of point-sized sources of light, the total variation in the amount of light entering our eye from more than one point sources will average out to zero, thereby nullifying the twinkling effectQuestion 12
Why does the Sun appear reddish early in the morning?Answer
Light of sun has to travel more distance in the atmosphere because it is very far from earth. All colour of lights get scatter except red colour due to longer wavelengths Therefore, the sun appears reddish at sunrise and sunset.
Question 13
Why does the sky appear dark instead of blue to an astronaut?Answer
Due to absence of atmosphere in space,scattering of light does not take place and sky appear dark instead of blue to an astronaut.
Chapter shortcuts
- Chapter 1 · Chemical Reaction And Equations
- Chapter 2 · Acids, Bases and Salts
- Chapter 3 · Metals and Non-metals
- Chapter 4 · Carbon and Its Compounds
- Chapter 5 · Periodic Classification of Elements
- Chapter 6 · Life Processes
- Chapter 10 · Light Reflection and Refraction
- Chapter 11 · Human Eye and Colourful World
- Chapter 12 · Electricity
- Chapter 13 · Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 14 · Sources of Energy
- Chapter 15 · Our Environment
- Chapter 16 · Sustainable Management of Natural Resources